|
|
|
| This article is available in: English Castellano ChineseBig5 ChineseGB Deutsch Francais Nederlands Turkce Korean |
![[Photo of the Author]](../../common/images/Manuel-B.jpg) by About the author: He's presently studying computer science at the Polytechnic University of Valence, Spain, where he spends most of his time. He's been loving Linux (and, generally speaking, Unix*) since when he started to use it, 5 years ago, and he loves everything connected to computers architecture. Far away from computers, he likes listening to music, going to the theatre, and snowboarding. Content: |
![[Ilustration]](../../common/images/illustration59.gif)
Abstract:
Resume: The F-CPU project attempts to develop a microprocessor like the present ones (Pentium II, Merced), following a development scheme close to the one guiding important free software projects. You might find this a utopia, but some points might make it come to a reality.
Yes. You read right. The word "cpu" actually means the traditional acronym: central processing unit, and not some other thing one might imagine reading the title. And, of course, the "F" stands for "Freedom". This is the project I will descrive in this paper. First of all, you must know that I won't give decisions of design that were taken in this project, but I will show its organization and goals.
The F-CPU project was born at the end of the summer of 1998 (I do not know the very date since I still was on holidays ;) and was initiated by Broin Vibber and Andrew D. Balsa, with the intent to develop a microprocessor (as a matter of fact, its name is F1) that would be an alternative to the ones of the market, extending the idea of free software (GNU/GPL) to the hardware (without perhaps the same license, for legal reasons, but with a similar one). Of course, this does not mean that the computer will be distributed free of charge, since there are production costs you do not find in the world of software, but its implementation and architecture will be free, and its development model will be like that of software projects that use the GNU/GPL, that is to say, a development open to whoever wants to participate.
You might be skeptical about the project: Who will pay the production costs? Who will implement the computer, once designed? Since the computer won't be free of charge (we estimated a cost of USD 100), its sales will have to even out the production costs. The project being very young, we still don't have enough to wonder about. In any case, once designed, properly tested, and its power once analyzed, the rumor has it that some companies will make it. The fact that the F1 will be based on a better architecture, and not on improvements in the integration techniques, because at the time to build the chip, the technology to engrave at a scale of 0.25 microns (or even, possibly, less) will be available for cheap, will help this building.
|
|
Well, that's great, but what will happen with my Linux? Without it, I'm no good...
Regarding this point, the project is very clear. The chip will be especially made for Linux, and it won't, it will NOT be compatible with Winbugs (98, NT), and the Wine emulator won't work on it. As far as other operating systems are concerned, they keep the door open to a possible x86 emulator, and they don't mention anything about other OSes.
I'm looking forward to use a F1 in my mother board... When will it be available?
This depends, of course, of the future evolution of the project, but if everything goes smoothly, they hope the F1 will be there in 2000, and as far as the F2 is concerned...
Enough with the round of questions. Let's talk about some points of the project.
One of the effects of the F-CPU project was to initiate some alternative projects, regarding other aspects of the architecture of the personal computer, directly related to the F1, and it collaborates very nearly with them. Those projects include mother board aspects (what socket will the F1 use?... it should use socket 7, slot 1 and super 7...), tools we need to evaluate and simulate the F1.
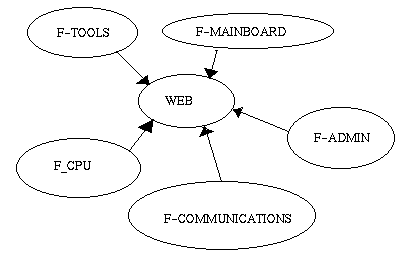 |
As you can see, the web is the principal coordinator of all the groups. Let's not forget the principal node of communication: the mailing lists (read at the end of the article to get more information), but we hope to get each developer to actualize through CVS the information of the web server.
Right now, the project is in its initial phase, when there are still few developers. There are nevertheless some people (we can especially cite AlphaRISC, KC5TJA, Andrew D. Balsa, Jecel Assumpcao Jr, Rafael Reilova, Steve Wilson,... and some others I don't remember, but they're in) who are already working on simulation tools, and the number of persons involved in the project, even though it doesn't grow in a spectacular way (it does, but that is another story), doesn't seem to decrease, if we consider there are still many people who do not know that project exists. In any case, the identities of the latest joiners show the project is interesting to people very good at hardware, VHDL, and simulation tools.
To finish, I will give you my personal point of view regarding the project :
| ...the f-cpu project seems more ambitious than those two projects (Gnome, KDE). |
Any way, like someone told me, this project can be a good learning place.
You will find there information regarding the project, the main lines, the documentation... Please take into account the fact this project is new and everything might not work as it should.
Original article in Spanish
Translated by Sébastien Blodeel
| Webpages maintained by the LinuxFocus Editor team © Manuel Benet Navarro, FDL LinuxFocus.org Click here to report a fault or send a comment to LinuxFocus |
2001-05-27, generated by lfparser version 2.15